Your digital payment security affects whether customers trust you enough to make online payments. Read on to find out why, and explore key best practices.
How Digital Payment Security Builds Consumer Confidence

44% of ecommerce customers have been the victim of payment fraud, with over 40% having experienced it twice or more. Even customers who’ve never been victims themselves, then, can struggle to trust online transactions. This erosion of customer confidence can lead to lost sales, customers, and loyalty, which is why digital payment security is so crucial.
Digital payment security encompasses the technologies, services, and strategies used to protect customers’ data while they’re making online payments. Let’s delve into how it helps you secure customer trust and walk through some steps you can take to implement enterprise-grade security into your digital payment environment.
What are digital payments?
Digital payments refer to any type of transaction that’s made online. It covers all digital payment touchpoints, including websites, mobile apps, social media, and digital wallets.
Customers favor digital payments because they offer convenience, flexibility, and speed. It empowers them to make digital payments directly from their device. This is facilitated by digital wallets like Apple Pay, Google Pay, PayPal, and Venmo, along with payment gateways like Stripe and Square.
There’s one significant obstacle that makes customers hesitant to make purchases online, though, and that’s cybersecurity.
TLDR
- With 44% of e-commerce customers having experienced payment fraud, building trust through robust security is essential to prevent lost sales and loyalty.
- Digital payment security involves key technologies like end-to-end encryption, tokenization, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to protect sensitive customer data.
- Beyond technology, building confidence requires proactive strategies, including third-party risk management, compliance with standards like PCI DSS, and using advanced AI-powered fraud detection systems.
Summary
This article explores why digital payment security is crucial for building consumer confidence in an age of rising cyber fraud. It identifies common threats like phishing and card skimming and outlines key best practices for businesses, including data encryption, tokenization, multi-factor authentication, and regulatory compliance, to create a secure and trustworthy online payment experience.
📑 Table of Contents
How digital payment security increases customer trust
Cyber fraud is a prevailing threat that’s at the forefront of your customers’ minds when they make digital payments.
63% of customers are “very” or “quite” concerned about cyber fraud when shopping online. Their biggest obstacle to trusting digital payments is the possibility of being hacked, followed by the possibility of being the victim of a data breach, or being scammed:
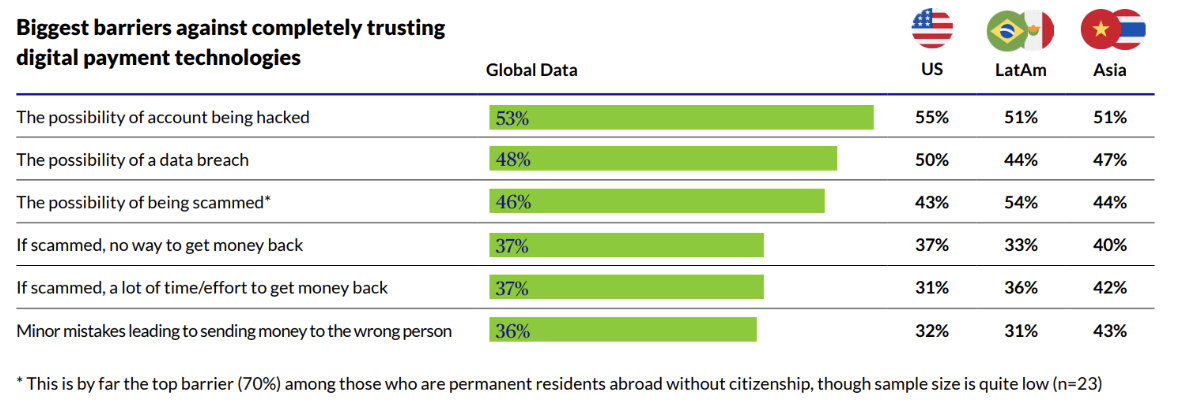
Image sourced from Chubb
Implementing digital payment security measures helps you defend online accounts and transactions against cyber fraud. With the threat landscape growing more vast and complex, businesses must win customer trust by understanding the tactics used by fraudsters and implementing security measures to combat them.
Some of the most prevalent types of cyber fraud include:
- Phishing scams: In a phishing attack, a scammer will pose as your business (often by using a fake email or website). Their goal is to trick the customer into handing over their sensitive details, such as credit card details, bank account information, or login credentials.
- Electronic card skimming: Hackers can secretly install credential-stealing software onto your website. When customers enter their card details to make a transaction on your site, the hacker can capture the data they enter and use it to commit credit card fraud.
- Credit card fraud: Credit card fraud occurs when a hacker who has gained access to a victim’s card details (via phishing, card skimming, or another method) uses them to commit fraudulent purchases.
- Account takeover: In an account takeover attack, a fraudster gains access to a user’s online account. This could be by exploiting security vulnerabilities on your website or app, or by stealing the login credentials of the user via a phishing attack or data breach. From there, they can change details like phone numbers or email addresses to make fraudulent transactions.
If your customers’ data is exposed or exploited, whether through a data breach or cyber fraud, your brand is going to take a huge reputational hit. So, it’s crucial that customers are protected across every touchpoint, from mobile apps and online stores to the digital wallets, credit cards, and devices they use.
Sometimes, it isn’t enough to simply implement security measures. Customers rely on visible security signifiers, such as SSL certificates, PCI compliance assurance, and trusted payment gateways, to validate your trustworthiness.
Key digital payment security best practices for building customer trust
Digital payments present cybersecurity challenges that erode customer trust. Integrate robust security measures across your organization’s digital payment environment, however, and you can foster faith in your business and maintain loyal customers.
So, what strategies should you implement to maximize digital payment security? Here are some best practices:
Data encryption
Encryption safeguards sensitive payment data, such as bank account details, credit card numbers, and security codes, by scrambling the plaintext into ciphertext. This makes it unreadable to unauthorized parties, preventing data breaches and ensuring payment information remains confidential.
Ensure the platforms and apps you use to store and transmit sensitive payment information offer end-to-end encryption. Look out for SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) to protect payment data as it’s transmitted over the internet, and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) to encrypt data at rest.

Tokenization
Tokenization technologies replace sensitive data with a unique token. That’s essentially a non-sensitive string of randomly generated characters. Having no mathematical relationship, tokens are irreversible, undecipherable, and rendered useless to unauthorized parties.
The relationship between the sensitive data and the token is stored in a highly secure external database known as a token vault. When processing payments, the system will use the token rather than the original payment information, preventing sensitive data from being exposed.
Multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) prompts a customer to provide two or more types of verification when accessing their online account and/or making digital transactions. This typically includes a password or PIN, as well as authenticators like:
- One-time passcodes (OTPs) delivered via SMS or phone call
- Email verification codes
- Push notifications
- Security tokens
- Biometrics, such as fingerprints or facial recognition.
Passwords are the first line of defence against cyber threats, but they have critical flaws. Cybercriminals have a stockpile of nefarious tactics up their sleeves that enable them to crack weak passwords in seconds.
MFA reduces the risk of breaches by implementing additional layers of security. It protects customers from common consumer scams and ensures that digital transactions are legitimate.
Recent research by Microsoft reveals that 99.9% of compromised accounts don’t have multi-factor authentication, highlighting just how important it is to modern security:

Data sourced from Microsoft
Risk management
Your business might be fortified with enterprise-grade security, but what about the vendors and service providers you partner with? To gain your customers’ confidence, you need to take dedicated steps to identify, assess, and mitigate the security risks and vulnerabilities posed by third-party partners.
This includes your ecommerce platform provider as well as payment gateway, payment processor, and digital wallet providers.
Third-party risk management tools can help here. They reduce vendor risks by automating vendor assessments, centralizing data across your digital relationships, and performing ongoing monitoring. So, you can create accurate risk profiles, conduct in-depth risk assessments, and continuously monitor the security measures of vendors to ensure they meet your expectations.
Compliance with industry standards
Complying with industry standards is essential, and not only for securing customer trust. It protects you from falling victim to cyber attacks and security breaches that can have serious financial and legal repercussions.
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of rules and guidelines that ensure companies follow security best practices when storing, processing, and transmitting credit card information. It was created by Visa, Mastercard, American Express, and a few other major credit card companies.
PCI DSS mandates that businesses implement security measures like:
- Firewalls
- Data encryption at rest and in transit
- Regular software updates
- Strong password protections
- Restricted access to cardholder data.
By complying with PCI DSS, you enhance cardholder data protection, prevent fraud, and communicate to customers that you’re committed to securing their sensitive data during online transactions.
Other regulations you should strive to comply with include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Payment Services Regulations (PSRs).
Fraud detection
Advanced fraud detection systems monitor real-time transactional data to identify suspicious activity and alert you in real-time, playing a critical role in fraud prevention. Their widespread adoption is a key reason why 56% of businesses can detect fraud at the point of transaction, rather than after the transaction has occurred, which has reduced from 17% to 12%, according to Alloy research:
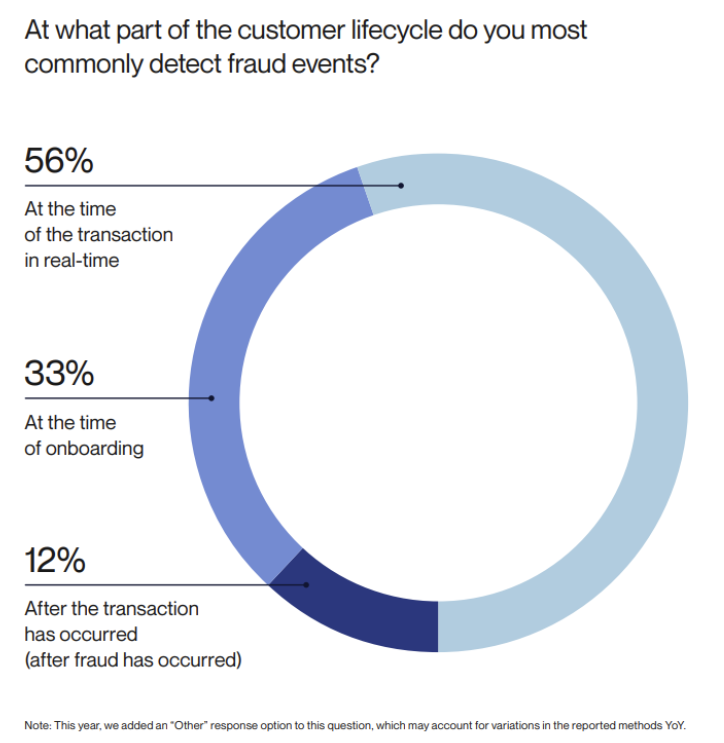
While rules-based fraud detection can still be useful, AI-powered fraud detection offers the highest degree of security.
AI and machine learning fraud detection can monitor and analyze vast volumes of complex transactional data at lightning speed, enabling them to spot patterns and anomalies much faster than humans. In doing so, they can prevent fraudulent payments before they occur, protecting customers from financial losses if their sensitive data has been compromised.
Comprehensive security audits
Conducting regular security audits instills customer confidence by assuring customers that you’re proactive in your mission to identify and address risks. But precisely what is a security audit?
A security audit is a comprehensive evaluation and analysis of your business’s systems, processes, and data in relation to cybersecurity. Specifically, it aims to identify potential security vulnerabilities and threats for the purposes of mitigating risks and enhancing security across your organization.
In the context of digital payments, a security audit would involve:
- Checking and updating payment data security controls, such as end-to-end encryption and tokenization.
- Testing network and endpoint security to protect against malware, card skimming, brute-force attacks, and other malicious activities.
- Assessing authentication and access controls.
- Analyzing and updating fraud prevention and detection technologies and processes.
- Evaluating compliance with regulations, ensuring adherence to updated rules and guidelines.
- Ensuring that employees are trained in cybersecurity. For example, knowing how to spot and respond to suspicious transactions, identify phishing emails, and create secure passwords.
Build consumer confidence with digital payment security
Data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and tokenization are just some of the lines of defence you can use to prevent cyber fraud. That said, digital payment security is about more than protecting customers at the point of purchase. It involves mitigating fraud through the proactive implementation of preventative measures, such as risk assessments, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance.
In doing so, you can create secure online shopping and digital payments experiences that your customers can trust, boosting your reputation along with sales, revenue, and loyalty.
Written by
Conor Byrne




